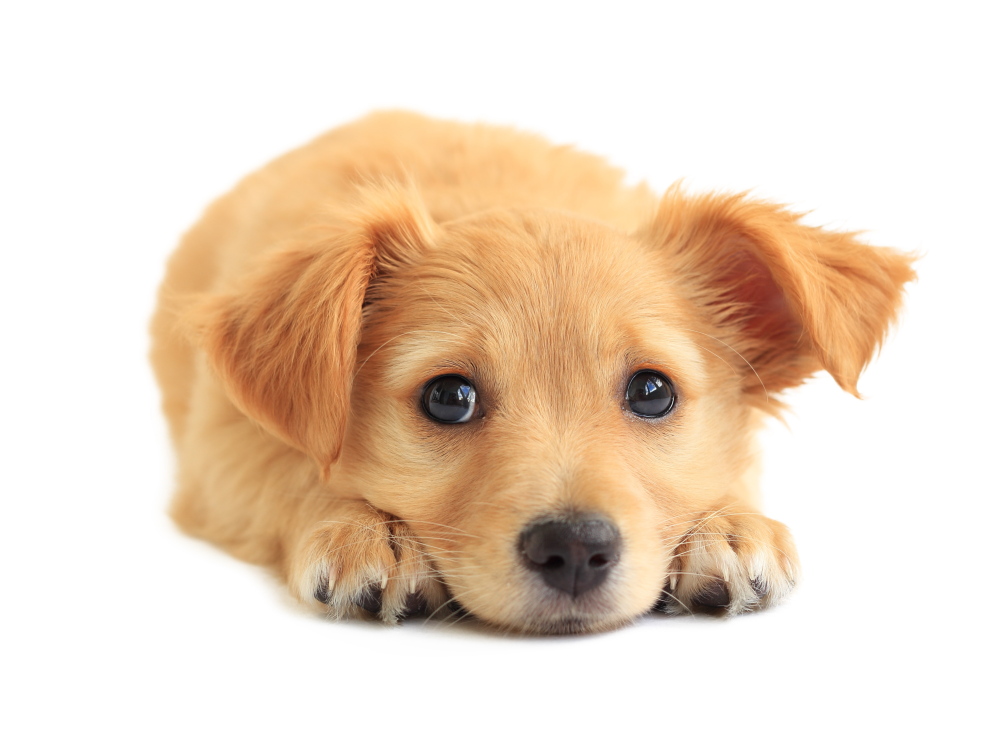
When you hear a friend’s voice, you immediately picture her, even if you can’t see her. And from the tone of her speech, you quickly gauge if she’s happy or sad. You can do all of this because your human brain has a “voice area.” Now, scientists using brain scanners and a crew of eager dogs have discovered that dog brains, too, have dedicated voice areas. The finding helps explain how canines can be so attuned to their owners’ feelings.
“It’s absolutely brilliant, groundbreaking research,” says Pascal Belin, a neuroscientist at the University of Glasgow in Scotland, who was part of the team that identified the voice areas in the human brain in 2000. “They’ve made the first comparative study using nonhuman primates of the cerebral processing of voices, and they’ve done it with a noninvasive technique by training dogs to lie in a scanner.”
The scientists behind the discovery had previously shown that humans can readily distinguish between dogs’ happy and sad barks. “Dogs and humans share a similar social environment,” says Attila Andics, a neuroscientist in a research group at the Hungarian Academy of Sciences at Eotvos Loránd University in Budapest and the lead author of the new study. “So we wondered if dogs also get some social information from human voices.”
To find out, Andics and his colleagues decided to scan the canine brain to see how it processes different types of sounds, including voices, barks and natural noises. In humans, the voice area is activated when we hear others speak, helping us recognize a speaker’s identity and pick up on the emotional content in her voice. If dogs had voice areas, it could mean that these abilities aren’t limited to humans and other primates.
So the team trained 11 dogs to lie motionless in a functional magnetic resonance imaging brain scanner, while wearing headphones to deliver the sounds and protect their ears. “They loved doing this,” Andics says, adding that the pooches’ owners were there to reward them with treats and petting. The scanner captured images of the dogs’ brain activity while they listened to nearly 200 dog and human sounds, including whines, cries, playful barks and laughs. The scientists also scanned the brains of 22 human subjects who listened to the same set of sounds. Both dogs and humans were awake during the scans.
The images revealed that dog brains have voice areas and that they process voices in the same way that human brains do, the team reported online Thursday in Current Biology. And because these voice areas are found in similar locations in the brains of both dogs and humans, the scientists suggest that they likely evolved at least 100 million years ago, when humans and dogs last shared a common ancestor, an insectivore. Indeed, some think that brain areas for processing vocal sounds could be discovered in more species.
Still, when voice areas were first discovered in humans, they were thought to be special and somehow tied specifically to the evolution of language. “So what are they doing in dog brains?” Andics asks.
The answer lies, he thinks, in what the scans also revealed: Striking similarities in how dog and human brains process emotionally laden sounds. Happy sounds, such as an infant’s giggle, made the primary auditory cortex of both species light up more than did unhappy sounds, such as a man’s harsh cough. “It shows that dogs and humans have similar brain mechanisms for processing the social meaning of sound,” Andics says, noting that other research has shown that dogs “respond to the way we say something rather than to what we say.” The similarity in auditory processing, he adds, “helps explain why vocal communication between the two species is so successful.”
But there were differences, too. The researchers discovered that in dogs, 48 percent of their auditory brain regions respond more strongly to environmental sounds, such as a car engine, than to voices. In humans, in contrast, a mere 3 percent of their sound-sensitive brain regions lit up more for the nonvocal sounds. “It shows how very strongly attuned the human auditory cortex is to vocal sounds,” Andics says. “In dogs, it’s more heterogeneous.”
Yet it is the similarity in how dogs and humans process the emotional information in voices that other researchers find most intriguing. “They’ve confirmed what any dog owner knows-that their pooches are sensitive to one’s tone of voice,” says John Marzluff, a wildlife biologist at the University of Washington. Even more important, he adds, is that the study “confronts us with the realization that our wonderful brain is in many ways a product of our distant evolutionary past.”
This is story is provided by AAAS, the nonprofit science society, and its international journal, Science.
Send questions/comments to the editors.


Success. Please wait for the page to reload. If the page does not reload within 5 seconds, please refresh the page.
Enter your email and password to access comments.
Hi, to comment on stories you must . This profile is in addition to your subscription and website login.
Already have a commenting profile? .
Invalid username/password.
Please check your email to confirm and complete your registration.
Only subscribers are eligible to post comments. Please subscribe or login first for digital access. Here’s why.
Use the form below to reset your password. When you've submitted your account email, we will send an email with a reset code.